How 2020 has affected insurance consumer behaviour in Sweden

The 7th edition of the Global Consumer Study looks at the impact of Covid-19 on protection needs and changing attitudes to health, mental health and digital usage. This year sees a new market added to the list of countries surveyed: Sweden.
The GCS team made this decision to capture consumer sentiment in Northern Europe/Scandanavia, also given the different approach to handling Covid-19 in the country. It's also a unique market with a centralised and well-developed insurance sector that has a strong appetite for technology. Despite an uncertain and complex environment, the report reveals some insightful findings about the Swedish market. While there are new opportunities to engage with policyholders, insurers must do more to convince Swedish consumers of the value of digital transformation, data sharing and even of insurance itself.
-
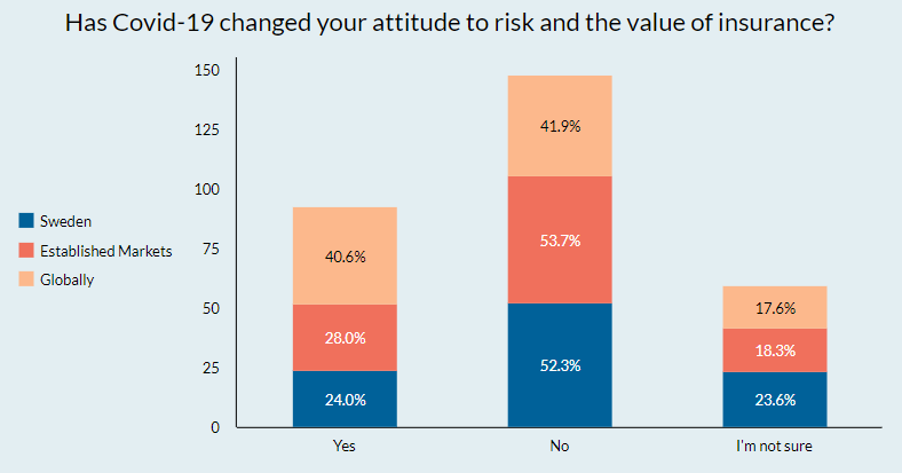
1 in 4 Swedes changed their minds on the value of insurance due to Covid-19
-
45.5% completed their insurance purchase via contactless channels
This year has seen profound global shifts, especially in attitudes towards health and digitisation, and had a significant impact on consumers. Studies have shown Covid-19 has caused to an increase in mental health issues and in our survey Sweden had the highest prevalence of self-reported mental health issues of any country. The same is true for diagnosed issues, especially among young, female consumers.
Yet in other ways the pandemic has had less of an impact in Sweden than elsewhere. Only 1 in 4 Swedes changed their minds on risk and insurance because of Covid-19 compared to 40.6% globally, aligning with results from other established [1] markets. Swedes are also less inclined to have become more proactive about health because of Covid-19 and fewer have made lifestyle changes (hygiene, travel etc.).
Consumers today use a broad range of channels to research, interact and purchase and this year has highlighted the importance of integrating digital channels into the customer journey. More Swedes completed their insurance purchase via contactless channels [2] this year than the global average (45.5% compared to 42.3%), and the fact only 1 in 4 changed their preference for online services because of Covid-19 shows how digitised the Swedish market was even before this year. At the points of the customer journey, however, when a human touch is needed (claims, customer service), Swedes are more comfortable and trusting of human interaction than automated services.

The findings show the importance of a seamless online-to-offline approach that integrates a human dimension to build trust. Brand awareness in Sweden remains strong, shown by the fact most respondents said insurance companies were their preferred source to research about life insurance, compared to family and friends or Professional Financial Adviser.
The GCS makes it clear that health is a top priority, and Swedes appear better than the global average on most health metrics surveyed. There is broad support across all demographics for insurers to do more in terms of health and wellness, and extend their proposition beyond death benefits. Data from integrated wellness programmes can also be used for dynamic underwriting, presenting new ways to assess risk and manage conditions. Around half of Swedish consumers would be willing to share electronic health records with their insurer, below the global average of 65.4%. There is clearly an opportunity for insurers to build engagement solutions that feature apps or wearable devices, given that ownership is less in Sweden than elsewhere.
The pandemic is a true marathon, and as we look to the future, its full effects on our society remains to be seen. Visit our GCS page to find more consumer insights and a dashboard to explore all the data.
[1] Established market refers to those countries often characterised by less growth and higher insurance spending per GDP (according to OECD figures). In this study established markets include Australia, Canada, France, Germany, Japan, Ireland, South Korea, Spain, Sweden, the US and the UK.
[2] Contactless channels include online search engine, company website, social media and other direct channels such as telephone and mailings.